COVID-19
Random
👵🏻 Some people have noted that after COVID-19 infections, people get all kinds of diseases at rates comparable to older people. I also feel like I’m “younger” than my grandparents were at my age. (I absolutely cannot imagine my grandmother going on a 45km bike ride at my age, for example.)
Knowing what I do now, I wonder if aging is due in part to heavier and heavier burdens of viruses — from depleting the reservoir of immune cells, from damage during the acute phase, and from chronic infections (like from herpesviruses). I got a whole bunch of childhood vaccinations that my grandparents didn’t get — polio, measles, mumps, rubella.
🌡️ This article (2020-01-07) about this paper from USA (2020-01-07) reports that human body temperatures have dropped by about 0.03°C per birth decade over a 157-year span. One of the theories they gave for why is that we just aren’t as sick all the time as we used to be!
🐁 This paper from Japan (1991) says that mice who are raised in germ-free environments live about 17% longer than mice who aren’t but this paper (2016) reports that mice who are raised without exposure to “good” bacteria have problems stemming from a poor gut biome. It might be that mice who get good gut bacteria but don’t get virus exposure live even longer, but I couldn’t find any papers which reported on yes bacteria / no virus experiments.
💉An obvious way to reduce the number of viruses that you are exposed to is vaccines. I have (mostly) stopped talking about very early stage trials, but what I see is that vaccine research is moving very swiftly. I think by ten or twenty years from now, we will have really good vaccines for all of the bat coronavirses, all the influenzas, MERS, malaria, HIV, Epstein-Barr virus, HSV-1, Zika, Chagas disease, and many more.
Even if better vaccines don’t slow aging, with a vaccine for Epstein-Barr virus, we will eliminate Multiple Sclerosis. With a vaccine for HSV-1, we might eliminate Alzheimer’s. Won’t that be nice?
US Politics Effect on Canada
🇨🇦🇺🇸✈️ Last week I linked to an article which said that air travel bookings from Canada to the USA were down by 70%. A Loyal Reader (JRP) found this article (2025-03-28) which says that article is just flat wrong. Bookings are down a little, but nowhere near 70%.
This article (2025-03-28) says that return flights to Canada are down by about 13% from last year. This article (2025-03-31) says that bookings are down by about 10%. This article (2025-03-31) says that WestJet has cut flights from Kelowna to Las Vegas and Seattle, but that domestic flights are up by 15%.
This article (2025-03-31) says that leisure destinations are getting hit hardest, with Florida at the top of the list. It says business destinations are not getting hit as hard. Interestingly, Honolulu didn’t see a decrease.
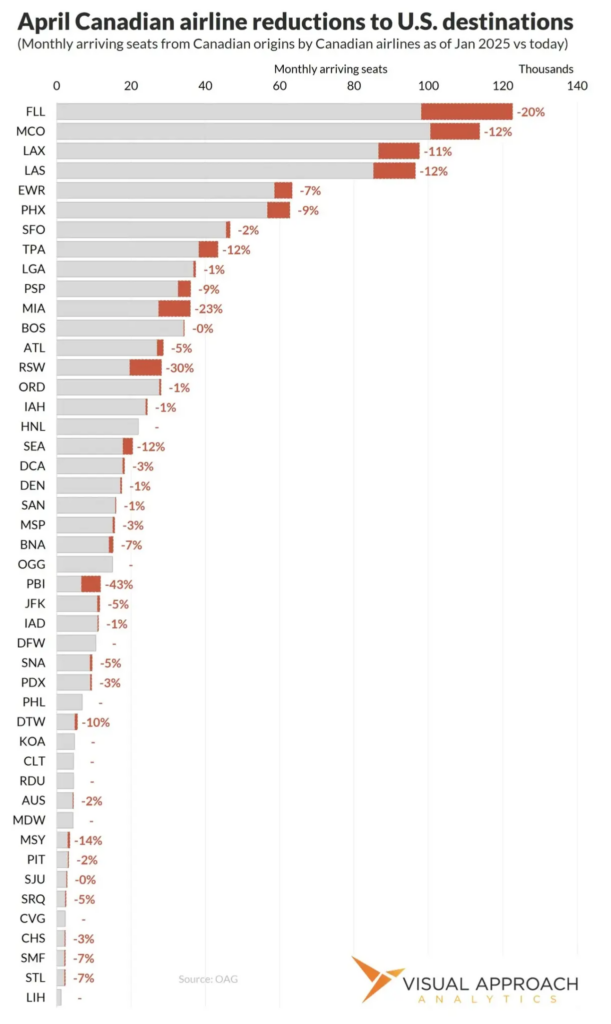
Okay, I’m probably not going to talk about planes any more.
This article (2025-03-31) says that some Canadian doctors are cancelling plans to move to the US, a lot fewer Canadian doctors are interviewing in the US, and a lot of US doctors are trying to come to Canada.
🤯😲 This article (2025-03-02) says that 75% of US researchers surveyed, especially early-stage researchers, are considering leaving the country.
Healthcare System
🧑⚕️🤧 This paper from Greece (2025-03-28) reports that COVID-19 accounted for 76.5% of total days missed by healthcare workers due to infectious diseases. Influenza accounted for 9.7% of the days, and everything else accounted for 13.8%. (For those of you who don’t have a calculator handy, that means that there were almost eight times as many days missed for COVID-19 as for influenza. COVID-19 is not the flu!)
The paper also mentioned that 14.9% of the HCWs came in sick (“presenteeism”), compared to 12.9 episodes per 100 HCW of being absent.
Long COVID
😢👶 This preprint from USA (2025-03-30) reports that children are slightly more than twice as likely to get Long COVID from their second COVID-19 infection as from their first. The risk of getting specific long-term symptoms from their second infection, compared to from their first infection, was:
- myocarditis: 3.60x;
- changes in taste and smell: 2.83x;
- inflammation of veins due to blood clots thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis/pulmonary embolism: 2.28x;
- heart disease: 1.96x;
- acute kidney injury: 1.90x;
- generalized pain: 1.70x;
- arrhythmias: 1.59x;
- fatigue and malaise: 1.50x;
- musculoskeletal pain: 1.45x;
- abdominal pain: 1.42x;
- postural orthostatic tachycardia syndromes (POTS)/dysautonomia: 1.35x;
- cognitive functions: 1.32x;
- respiratory signs and symptoms: 1.29x.
😢 This paper from Hong Kong (2025-03-28) found that children with Long COVID tested significantly lower in language skills, both in their first language (Chinese) and second language (English). It was worse the older the students were.
⁉️🤰This paper from USA (2025-04-01), unlike the paper from Singapore (2025-03-10) which I summarized last week, says that pregnant women were 24% to 30% less likely to get COVID-19 than matched non-pregnant women.
A reminder (because I couldn’t remember and I wanted to know): this paper from USA (2024-07-17) said that the number of people getting Long COVID has changed over time. Here are the number of people who got Long COVID per 100 people who got COVID:
| Pre-Delta | Delta | Omicron | |
| unvaccinated | 10.42 | 9.51 | 7.76 |
| vaccinated | N/A | 5.34 | 3.50 |
COVID-Related Excess Deaths and Sickness
🍆 This paper from China (2025-04-03) reports that sperm quality of men who had COVID-19 is much lower than that of uninfected men on a number of measures. For example, comparing sperm samples taken from the same men pre- and post-COVID:
- 59.3% had lower sperm concentration;
- 57.9% had lower sperm count;
- 71.4% had lower Grade A sperm count;
- 65.0% had lower progressive motility;
- 69.3% had lower total motility;
- 75.0% had lower sperm DNA fragmentation index.
You might object that the men got older over that time period, so their sperm would degrade in quality anyway, but non-infected controls had changes that were all less than a 40% reduction.
This paper from Taiwan (2025-03-29) reports that compared to influenza patients, COVID-19 patients had double the risk of advanced chronic kidney disease and triple the risk of acute kidney injury.
🤧 This paper from USA (2025-04-01) reports that people who tested positive for COVID-19 had more illness afterwards than people who didn’t. Compared to people who didn’t have a positive test (from November, 2021 to December, 2023) later had:
- 17% higher risk of outpatient diagnosis of infectious illness (bacterial, fungal, and viral infections);
- 46% higher risk of outpatient respiratory infections;
- 41% higher risk of hospital admission for infectious illnesses.
Compared to people who had been admitted to hospital for influenza, people admitted for COVID-19 later had:
- 24% higher risk of admission to hospital for infectious illness;
- 35% higher admission to hospital for sepsis;
- 23% higher risk of in-hospital use of antimicrobials.
Pathology
👶⚡️ This paper from South Korea (2025-03-27) found that 22% of pediatric patients who came to the ER or outpatient clinics who were diagnosed with COVID-19 at seven hospitals during Omicron had seizures. (NB: I can’t tell if they were admitted to hospital or not, it just says they were diagnosed at hospitals.) By contrast, only 0.3% who were pre-Omicron had seizures.
🩸 This paper from USA (2025-03-31) reports that among patients who were admitted to hospital with gastric bleeding, patients with COVID-19 did much worse. The in-hospital mortality rate of COVID-19 patients with an upper GI bleed was 2.5 time that of non-COVID bleeders. Bleeding patients with COVID-19 also needed more interventions: more blood transfusions, more steroids, more proton pump inhibitors, and more immunosuppressants.
Transmission
🤧🤧 This preprint from Kenya (2025-03-27) reports that with detailed surveillance of a bunch of people, they found that 180 got COVID-19, and five of them got it a second time in very quick succession — between 16 and 95 days. Four of them got sick with the exact same lineage that they’d been sick with before. So much for “natural” immunity.
Mitigation Measures
😷🤯 This paper from UK (2024-12-03) reports that, based on a statistical analysis, wearing respirators (i.e. FFP2 or N95 class masks) drops the effective reproduction number (R0) by a factor of NINE!
Vaccines
🎉💉 This preprint from USA (2025-03-28) reports that Moderna’s KP.2 booster is 53% effective against hospitalization for COVID-19 and 39% effective against seeking any medical treatment for COVID-19 (e.g. an ER visit), for about two months, compared to people who did not get a booster.
Remember, part of why that number looks low is because the comparison group (“people who did not get a booster”) includes a lot of people who had COVID-19 infections.
🎉 This preprint (2025-03-19) found that the COVID-19 spike protein with the two-proline stabilization (S-2P) acts as an adjuvant (something that increases the effectiveness of a vaccine). When an influenza antigen was given 👃intranasally to mice with S-2P, the mice were more resistant to influenza than when they were given a flu antigen without S-2P! 🤯
The article also mentioned that when the mice were given straight S-2P intranasally and then challenged with BA.5, 40% died, but when they added compound lentinan (which comes from shiitake mushrooms!) to the vax, all of the mice lived. 🎉
H5N1
Transmission
This article (2025-04-02) reports that the current total of infected dairy herds since March 2024 in the US is up to 996, which includes 758 from California.
This article (2025-04-02) reports that a two-year old in India died of H5N1 after eating raw chicken. They don’t know which clade she had.
Measles
Transmission
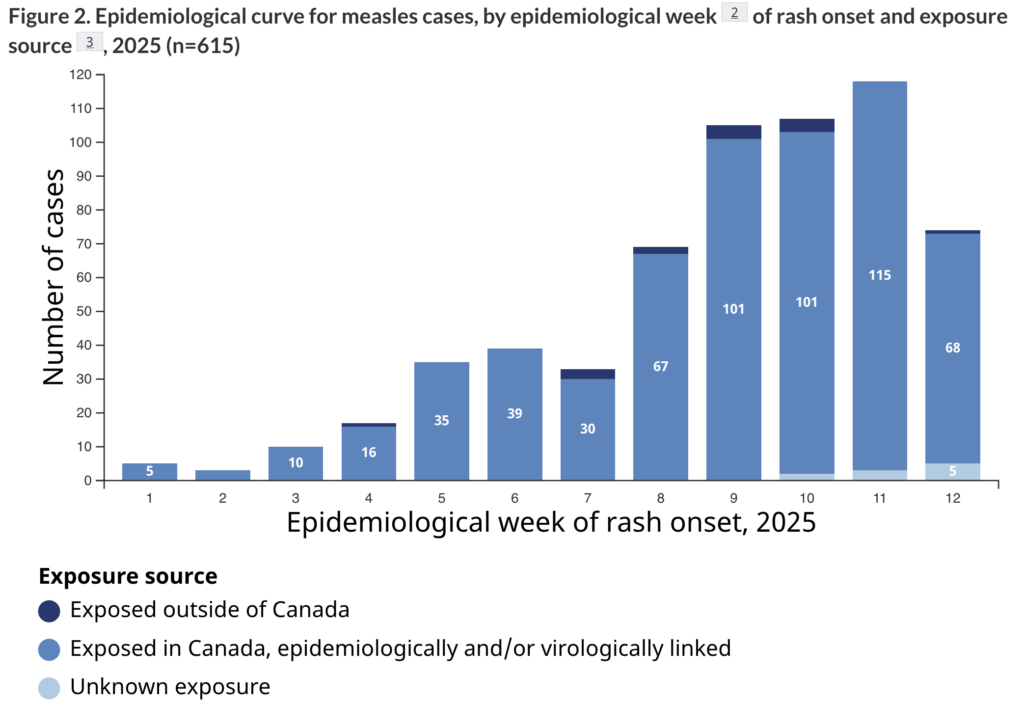
Yep, measles is still a thing. It’s out of control in the USA, but we’ve got some here, too. The PHAC measles updates page reports that from March 16 to 22, 2025, 119 new measles cases (104 confirmed, 15 probable) were reported. 80% have in unvaccinated people; ~13% in people of unknown vaccination status. Only ~6% were in vaccinated people.
Most are in Ontario (548 cases!). BC has had 5 cases, but none reported since 8 March.