Long COVID
Even people who don’t have classic “Long COVID”, getting COVID-19 is bad for you long-term. This paper from Florida reports that people who had COVID-19 have all-cause-mortality rates in the year after their acute phase at much higher than those who did not get COVID-19. Compared to people who were not infected with COVID-19, over the course of the following year:
- People who had severe COVID-19 were 2.5 times as likely to die;
- People who had mild cases were 1.87 times as likely to die;
- People under 65 who had severe COVID-19 were 3.33 times as likely to die;
- People under 65 who had a mild case of COVID-19 were 2.83 times as likely to die;
- People over 65 who had severe COVID-19 were 2.17 times as likely to die;
- People over 65 who had a mild case of COVID-19 were 1.41 times as likely to die.
Only ~20% of the deaths were from respiratory or cardiovascular illnesses, although for people who had severe COVID infections, the risk of respiratory-caused death was 4.58 times higher than for the uninfected group; the risk of cardiovascular-caused death was 3.13 times higher.
Transmission
This paper from the USA looked at transmission in prison settings with and without prior immunity. They found that, compared to people who caught COVID-19 with no prior exposure (infection or vax), people who had some immunity were less likely to transmit COVID-19:
- People who had any vaccination but no infection were 22% less likely to transmit;
- People who had been infected before but had not been vaccinated were 23% less likely to transmit;
- People who had been both vaccinated and infected before were 40% less likely to transmit;
- The likelihood of infection increased by 6% for every five weeks from the vaccination date.
- Additional booster doses gave 11% more protection for each dose.
This paper using data from France found that children were the biggest drivers in the early waves.
Pathology
This paper from India says that on almost every measure, pandemic sperm looked better than pre-pandemic sperm: higher concentration, higher count, higher percentage of motile cells. However, there was also a higher count of abnormal cells.
This paper from the US says that there wasn’t really any difference in the blood of people who got myocarditis after vaccination, except that those people had Spike protein in their blood, while controls did not. Note that the vax isn’t supposed to get into the blood — intramuscular injections are supposed to end up in the lymph system, not the blood system. (There was also some speculation that the AZ blood clots came from vax getting into the blood stream. I frequently ask the vaccinator to “aspirate”, which means drawing the plunger back slightly to make sure there is no blood in the needle, before injecting the vax.)
Testing
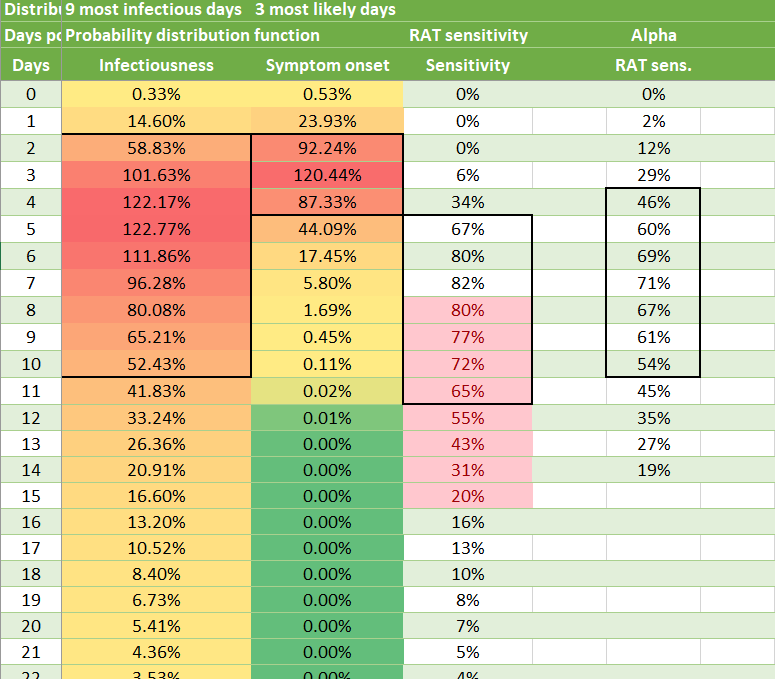
This table from this tweet says that RATs are really pretty horrible at keeping you from infecting other people. Note that on the third day after infection, the RAT was only 6% sensitive, but people were already wickedly contagious by then.
Treatments
This article (from November) reports that Japan has authorized a new protease inhibitor (Ensitrelvir, brand name XoCova for use against COVID-19. This press release from the manufacturer says that the manufacturer has applied for authorization in South Korea.
This paper from the USA reports good results in hamsters for a drug which works as an ACE2 decoy. My understanding is that they flood the body with the decoys, the virus latches on to enough of the decoys that transmission is slowed long enough for the body’s immune system to mop up.
Vaccines
This paper from the USA compared boosters of Pfizer Classic with Moderna Classic monovalents and found that the COVID-19 risks within sixteen weeks of a booster were higher with Pfizer than Moderna:
- 15% higher for documented infection;
- 21% higher for symptomatic infection;
- 64% higher for hospitalization;
- 37% higher for ICU admission;
- 8% higher for death.
I am guessing/presuming this is because Moderna has more mRNA in it than Pfizer does.
This paper from Australia found that vaccinating adults was more useful than closing schools at reducing spread.
This paper from the USA says that men who recovered from COVID-19 had stronger responses to a flu vaccine than either men who had not had COVID-19 or women (regardless of whether they’d had COVID-19 or not).
Last week I said that Medicago had cut ties with Philip Morris International, but I didn’t know how. This article says that Philip Morris sold all its shares to its partner, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma.
Wow, this paper from Israel says that if you get a bivalent booster, you are 81% less likely to get hospitalized and 86% less likely to die than if you did not get a booster.
