COVID-19
Vaccines
‼️🎉🐁🦷 Scientists have found an alternative method of giving mucousal vaccines: with dental floss! This paper (2025-07-22) found that flossing mice three times with floss covered with influenza virus, at two-week intervals, protected the mice from a lethal dose of influenza. All the mice who had been flossed survived, while all the unflossed control mice died:
Floss-based immunization induced strong and sustained immune activation across multiple organs, robust systemic and mucosal antibody responses, and durable protection against lethal influenza infection, independent of age, food and liquid consumption.”
I must admit that I am amused by the mental image of scientists flossing mice. (Apparently it takes two scientists to floss one mouse!)
💉🫀 This paper from Estonia (2025-07-29) reports that no, COVID-19 vaccines do not increase your risk of heart problems. In fact, vaccination dropped the risk of a major acute cardiovascular event by 29% and all-cause mortality by 68%.
Vaccines are good, actually!
💉 This paper from Denmark (2025-07-28) looked specifically at the safety of JN.1 mRNA vaccines, and found that they were really safe. They looked at 29 different diseases/conditions, and did not find a significant increase in any of them after vaccination compared to historical rates.
💉 This paper (2025-08-02) reports that COVID-19 vaccination decreases the risk of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS). (This surprised me because I (incorrectly) thought GBS was usually a side effect of vaccination!) However, it appears that COVID-19 infections cause GBS more often than COVID-19 vaccinations.
COVID-Related Excess Death and Sickness
‼️‼️😲😬🦀 This paper with data from UK, Germany, and Japan (2025-07-30) reports that, in mice, influenza or COVID-19 infections sometimes cause dormant cancer cells in the lungs to wake up and go wild, making cancerous lesions in the lungs in less than two weeks.
‼️‼️😲😬🦀 They also searched through the UK’s Biobank and Flatiron Health databases and found that COVID-19 infections substantially increased the risk death from cancer and lung lesion metastasis compared with cancer survivors without COVID-19. 😢
Viruses are bad for you!
This paper using data from UK and USA (2025-07-30) reports that in a large survey, symptoms of Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction (DGBI) have increased significantly compared to pre-pandemic:
- Overall, probable DGBIs have risen by 20%;
- esophogeal probable DGBIs have increased by 16%;
- gastroduodenal probable DGBIs have increased by 45%;
- bowel probable DGBIs have increased by 12%;
- probable functional dyspepsia symptoms have increased by 48%;
- probable irritable bowel syndrome symptoms have increased by 31%.
(I say “probable DGBIs” because the study authors basically diagnosed diseases based on the symptoms that the survey respondents described.)
Long COVID
🎉💉 This paper from USA (2025-07-31) reports that vaccines and some drug treatments reduce the risk of Long COVID:
- one COVID-19 vaccination: 23% risk reduction:
- two COVID-19 vaccinations: -27%;
- three COVID-19 vaccinations: -36%;
- four COVID-19 vaccinations: -71%;
- Paxlovid treatment: -95%;
- remdesivir: -69%.
💸 Surprise, surprise, this paper from USA (2025-07-29) found that the have-nots get Long COVID more than the haves. 😢 Different socioeconomic challenges increased the risk of getting Long COVID (even after adjustment for demographic characteristics, pregnancy, disability, comorbidities, SARS-CoV-2 severity, and vaccinations):
- financial hardship: increased the risk by 136%;
- food insecurity: +136%;
- less than a college education: +60%;
- experiences of medical discrimination: +137%;
- skipped medical care due to cost: +187%;
- lack of social support: +79%.
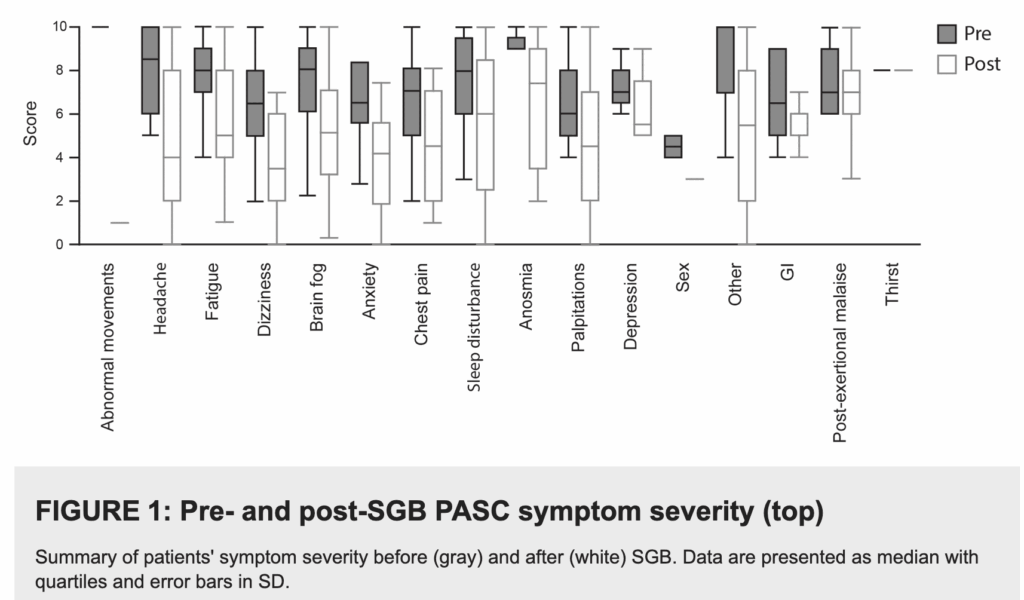
🎉 This retrospective paper from USA (2025-07-24) reports that stellate ganglion blocks (SGB) are useful. Most of the 52 Long COVID patients in the study (who got three SGB injections each) saw improvement:
Pathology
😬 This preprint from USA (2025-07-23) reports that children who had had COVID-19 infections had more autoantibodies than children who did not have COVID-19. This seems like a bad thing. (Reminder: autoantibodies are things that attack one’s own body.)
This paper from Hong Kong (2025-07-28) reports that hospitalized COVID-19 patients who had rebound did worse than hospitalized COVID-19 patients who did not have rebound. Different antivirals corresponded to different risks of post-acute mortality:
- all patients with rebound had 52% higher risk;
- patients who had rebound after taking Paxlovid or molnupiravir had a 78% higher risk.
‼️💪🛌 This paper (2025-07-31) reports that when scientists exposed lab-grown muscle to blood from ME/CFS or Long COVID patients for two days, the muscles developed fragility and fatigue.
Treatments
‼️🎉🥖💩 This small study from USA (2025-07-30) found that children with MIS-C who were treated with larazotide recovered faster than those who were given a placebo. (Note that these children were very sick. MIS-C is just awful.) It sped up the recovery from gastrointestinal symptoms, reduced the amount time it took to clear SARS-CoV-2 protein antigens from their stool (which I think means “reduced the amount of time which rapid antigen tests could detect SARS-CoV-2 in their poo), and got them back to normal activities faster.
Larazotide is a zonulin inhibitor, and zonulin is a protein that increases the permeability of cell walls in the gut. (Larazotide was originally developed as an anti-celiac drug, as gluten (or rather gliadin, a glycoprotein in gluten) causes more zonulin to be produced.) The thought is that pockets of SARS-CoV-2 hide in the gut, and if the gut is leaky, the SARS-CoV-2 can sneak into the bloodstream and cause havoc elsewhere.
There is some thought on teh socials that maybe larazotide will help Long COVID, too.
🎉💊 This preprint (2025-06-03) that 72% of Long COVID patients who took rapamycin got lots better.
This patient-led survey of ME/CFS and Long COVID patients (2025-07-08) reported very similar symptoms and responses to treatments between ME/CFS patients and Long COVID patients.
Alas, there was no treatment which only gave good results:
💊 It must have felt magical when Fleming showed that penicillin was a broad-spectrum antibiotic. That’s how I felt reading this paper (2025-07-31), which describes a broad-spectrum anti-viral. It’s only been tested in the lab, so it might not work in practice — maybe it’s lethally toxic, for example. But a girl can dream….
Transmission
‼️🏥😲😬 This preprint from Ontario (2025-07-28) reports that the growth of cases in a community did predict hospital outbreaks, but that hospital outbreaks predicted community case growth.
I remember saying to someone that I thought COVID-19 could be contained in elementary schools because “in hospitals, there are lots of different people coming and going, while in schools there’s a relatively small cohort of people who staying mostly in one room; they can contain infections in hospitals, so they ought to be able to contain infections in schools.” HAH! Boy, was I deluded in thinking that hospitals contained infections.
From Canada’s respiratory virus surveillance report (updated 2025-08-01):
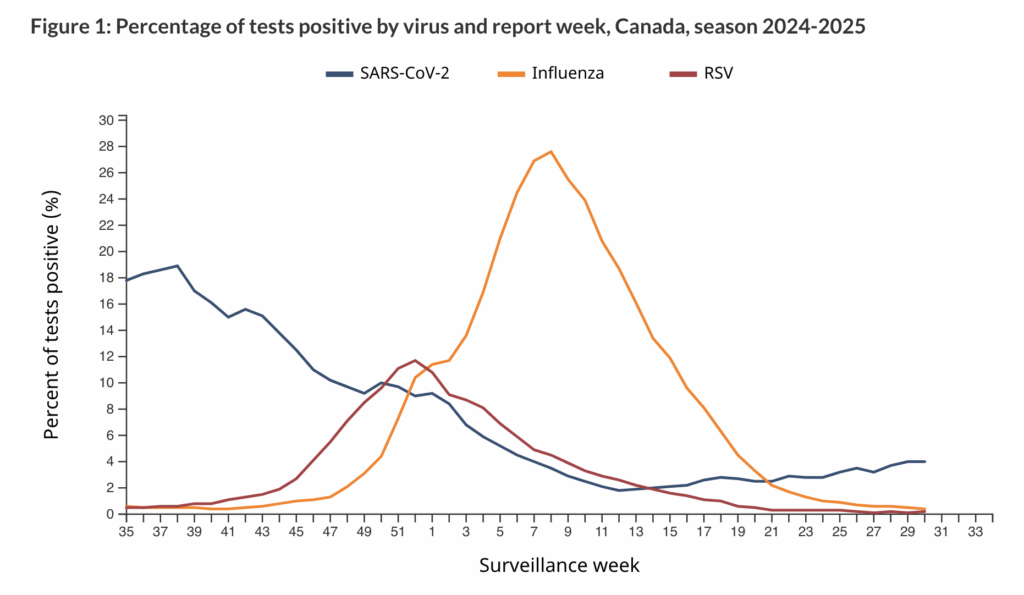
I was surprised to see that in Canada, enterovirus/rhinovirus is high right now, higher than COVID.
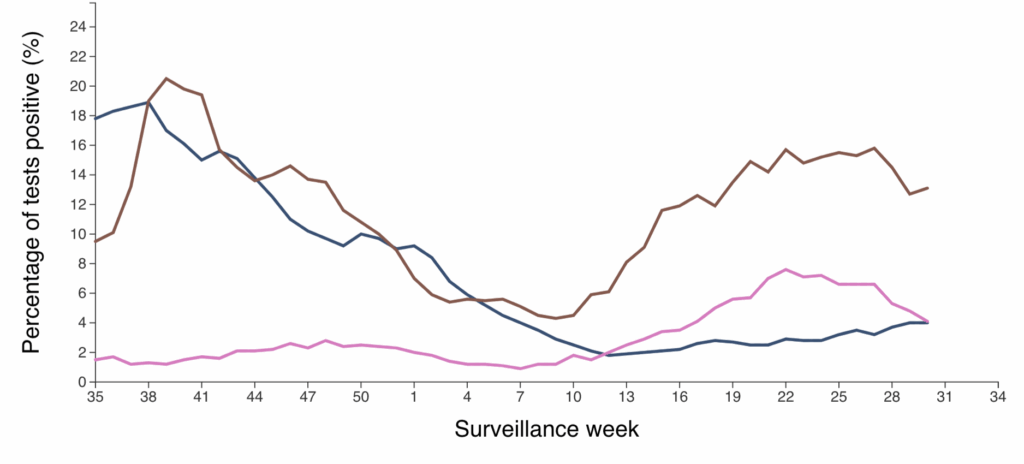
Reminder: BC will publish respiratory virus data next week.
Testing
BC Wastewater
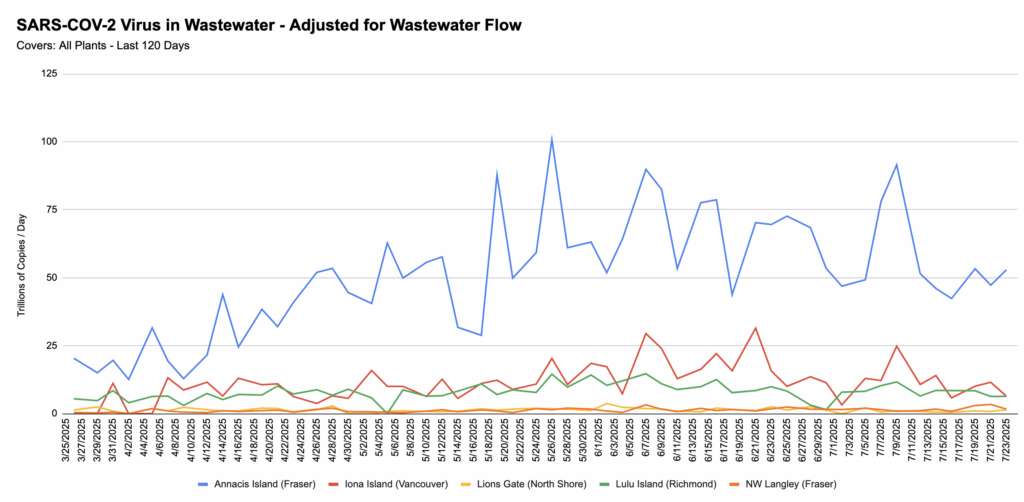
💩💧 Wastewater levels seem to be holding steady.
From Jeff’s wastewater spreadsheet:
Recommended Reading
🇸🇪 This article from USA (2025-08-01) talks about all the ways in which people are taking the wrong message from Sweden’s “no lockdowns” policy. A lot more elderly lived alone, people did what the government told them, the government got vaccines out really fast, and they had horrible, horrible death rates in 2020, to name just a few things. It points out that letting COVID run wild was an absolute disaster in Peru — a country which didn’t have Sweden’s advantages.
This isn’t COVID-19, but I don’t know where to put it and it’s wild. This article (2025-08-01) about this paper (2025-07-28) says that if people see someone contagious, their immune system starts prepping. They figured this out by measuring people who saw contagious-looking people in virtual reality!
Measles
Transmission
According to the Government of Canada Measles and Rubella Monitoring Report (updated 2025-07-28), in the week ending 19 July, the following jurisdictions had the following number of cases:
- Canada: 230;
- Alberta: 140;
- BC: 26;
- Ontario: 23;
- Nova Scotia: 21;
- Manitoba: 13;
- New Brunswick: 6;
- Saskatchewan: 1.
💉 This article (2025-07-31) mentions that Alberta does not have mandatory immunization requirements for school enrollment, and only 70% of children are fully vaccinated against measles there.
Don’t feel too smug: the BC Childhood Immunizations Dashboard says that as of 2023 (the last date available) only 72.4% of 7 year-old BC children were immunized against measles! Only 65.6% of 7 year-olds were up to date on all their recommended shots. In Vancouver, it was only 63.0%. 🙁

1 comment
Comments are closed.