COVID-19
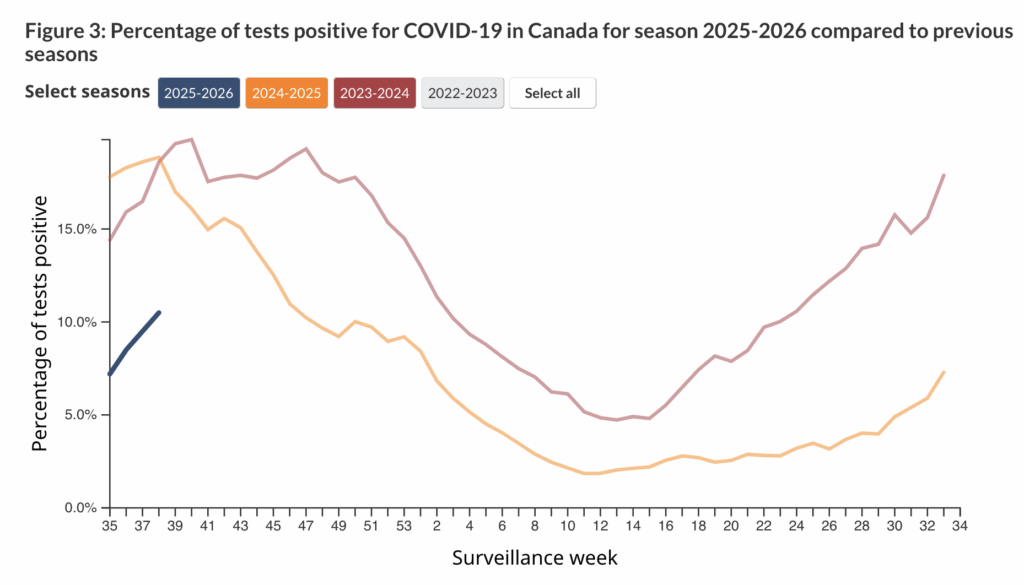
It’s a bit hard to tell what is happening with COVID-19 in BC because of the lack of data, but COVID-19 in Canada overall is definitely going up.
Long COVID
🫡 This paper from the USA (2025-09-16) looked at Long COVID in active duty service members and found:
- 0.05% of active duty service members per month got Long COVID. That’s about 0.6% per year.
- Women were 3.7 times at higher risk of getting Long COVID than men.
- People aged 55-64 were about 29 times more likely to get Long COVID than people aged 17-24.
COVID-Related Excess Death and Sickness
🫀💉 This paper from China (2025-09-14) reports that COVID-19 vaccines reduce the risk of coronary heart disease (which probably actually means that vaccines reduce the risk of COVID-19, and that COVID-19 increases the risk of coronary heart disease). The more doses, the more protective it was compared to only one dose, even when adjusted for race, sex, age, marital status, education, income, health insurance, smoking, BMI, food security, diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, depression, pulmonary disease, neighbourhood, and social determinants:
| # doses | unadjusted risk | adjusted risk |
| 2 | -32% | -32% |
| 3 | -47% | -38% |
| 4 | -61% | -36% |
| 5 | -69% | -39% |
| 6 | -89% | -50% |
🍞 Man, is there anything that COVID-19 does not raise the risk of?? This paper from China (2024-05-03) says that a COVID-19 infection raises the risk of celiac disease. 🦠 It mentions that people with severe COVID-19 have less Victivallaceae, a family of human gut bacteria which the paper says gives some protection against celiac disease.
This paper from Taiwan (2025-09-21) reports that people who got shingles within a year after a COVID-19 infection had higher risks of various things compared to people who had COVID-19 infections without shingles.
- 64% higher risk of getting leukopenia (decreased white blood cell count);
- 82% higher risk of getting a urinary tract infection;
- 3.8 times higher risk of getting multiple myeloma;
- 3.2 times higher risk of getting leukemia.
I don’t know what the risk is compared to people who {had shingles but not COVID-19 infections or something else (e.g. influenza) after COVID-19 infections}; the paper didn’t talk about those cases. Also, getting COVID-19 raises the risk of reactivating the shingles/chicken pox virus (as this review paper (2023-08-09) reports).
Get your shingles vaccinations, folks! (Or, if you haven’t had chicken pox, your chicken pox vaccinations!)
🧠 The results of a large survey from USA (2025-09-24) reports that cognitive disabilities have risen enormously since the start of the pandemic.
| cohort | 2013 prevalence | 2023 prevalence |
| all adults | 5.3% | 7.4% |
| 18 to 39 year-olds | 5.1% | 9.7% |
👃‼️ This paper from USA (2025-09-25) reports that people who had COVID-19 infections frequently had a measureable loss of smell — even a lot of the people who thought that their sense of smell was unaffected.
| what they thought | average percentile ranking | % with smel loss | % with severe smell loss |
| I lost smell | 16th | 79.8% | 23.0% |
| I didn’t lose smell | 23rd | 66.0% | 8.2% |
| I never had COVID | 28th |
Now, even the percentile ranking of the “I never had COVID” cohort is a bit odd, given that the average percentile in the population ought to be 50% (by definition!). The Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test has been around since at least 2007, so presumably the mapping from score to percentile ranking was done pre-pandemic. Does that mean that a lot of the people who said, that they never had COVID-19 actually did, and their smell suffered for it?
Mitigation Measures
🐶 This paper from UK (2025-09-17) investigated dog-child interactions for puppies bought (i.e. not from a shelter) right before or during the pandemic. It reports:
- 95% of the time, the person who took care of the dog most was the mom;
- Around 55% of the caregivers had previously had a dog;
- 37.3% of the caregivers found dealing with a puppy harder than they had expected;
- almost all children were allowed to interact with the dogs in ways which other research says increases the risk of getting bitten;
- 6.1% considered rehoming the dog:
- 85.7% of those were first-time dog owners;
- 47.1% of the 6.1% were due to reported poor behaviour of the dog, including poor socialization due to pandemic restrictions (most of the others had trouble with the time required or stress) ;
- 82.4% of the 6.1% found that the problems diminished as the dog matured and pandemic restrictions eased;
Testing
BC Wastewater
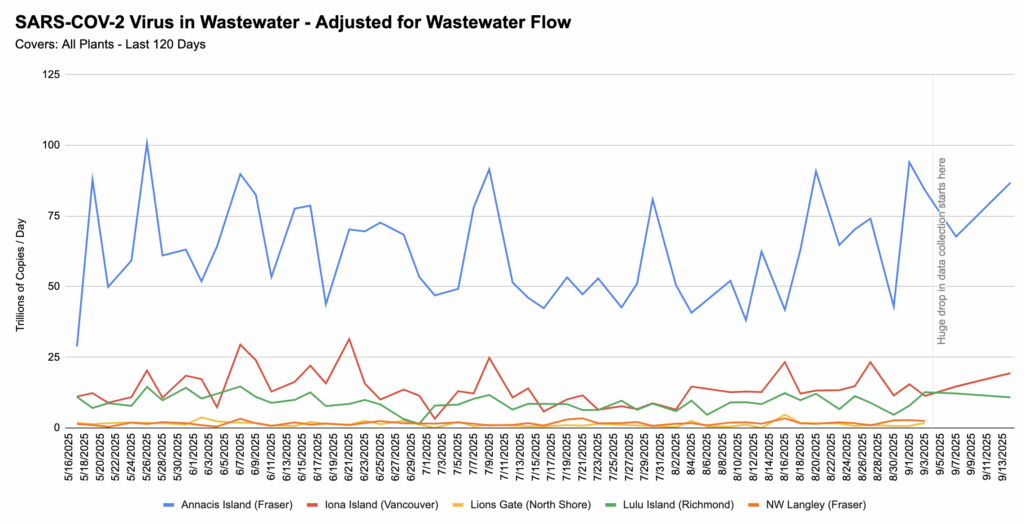
💩💧 From Jeff’s wastewater spreadsheet, with the drop in collections (which I mentioned last week) noted as the faint vertical line near the right.
RSV
Vaccines
🎉💉 Nirsevimab is not a vaccine, but it is a monoclonal antibody which gives relatively long-lasting (~6 months) protection against RSV, so it is used sort of like a vaccine. This large study using data from USA, Canada, Lebanon, and Saudi Arabia (2025-09-24) reports that the risk of hospitalizatio for RSV was about 70% lower in babies which got nirsevimab compared to those who did not get nirsevimab (and whose mothers did not get an RSV vaccination during pregnancy).
This paper with data from multiple countries (2025-09-22) reports that the monoclonal antibody clesrovimab works even better against RSV, with an efficiency of 82.4%.
Measles
Transmission
According to the Government of Canada Measles and Rubella Monitoring Report (updated 2025-09-22), in the week ending 13 September, the following jurisdictions had the following number of cases:
- Canada: 70;
- Alberta: 43;
- BC: 14;
- Nova Scotia: 8
- Saskatchewan: 7;
- Manitoba: 6.
This is up significantly from last week.
